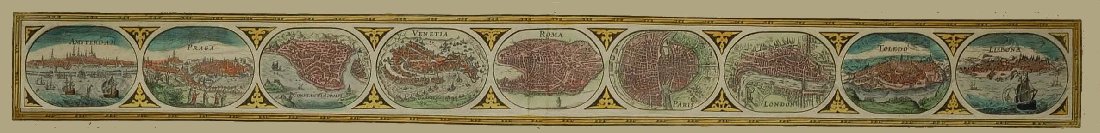
Kartograf som 1875 tog fram en tematisk karta där han jämförde befolkningen i Europa.
Bland arbeten.
Encyclopédie ou dictionnaire universel raisonné des connaissances humaines.
1703-1759. Född i Memmingen, Bayern.
Målare, gravör och konstruktionsritare. Anlände till St Petersburg 1741 tillsammans med gravören Johann Stenglein. Grimmel medverkade bl.a. i utgivningen av en 'Atlas Russicus' 1745 (Inte d'Isles atlas som kom samma år med samma namn.), samt gav även ut ett arbete i fyra blad 'Ladoga-kanal' 1741-42.
En av Grimmels elever vid vetenskapsakademin var Mikhail Makhayev.
Matthaeus Seutter gjorde kopior på vissa av Grimmels kartor så tidigt som under 1740-talet, bland annat 'Ingria et Carelia' samt 'Teshenije Nevy reky...'.
Bland arbeten.
Finskoj zaliv ot Kronshtata do Sanktpeterburga... = Der Sinus Finnicus von Cronstad bis St.Petersbürg benebst den aug seinen Kusten befindlichen Lusthöfen [engraved map] / J. Grimmel del. [St. Petersburg, c.1742].
Karta Ingermanlandii i Karelii. [The Academy of Sciences in St Petersburg]; Grimel del. - [St. Petersburg, c.1742].
Ladozhkoj kanal. Canalis Ladogensis [engraved map] / J. Grimmel del. [St. Petersburg, c.1742].
Ladozhskoe Ozero i Finskii zaliv s prilezhashchimi mestami. Lacus Ladoga et sinus Finnicus. [The Academy of Sciences in St Petersburg]; J. Grimel del. [St. Petersburg, c.1742].
Magnus Ducatus Finlandiae. [The Academy of Sciences in St Petersburg]; Grimel del. - [St. Petersburg, c.1743].
Techenije Nevy reky iz Ladozhgago ozera k St.Peterburgu = Fluwius Newa... [engraved map] / J: Grimmel del. - [St. Petersburg, c.1741-42].
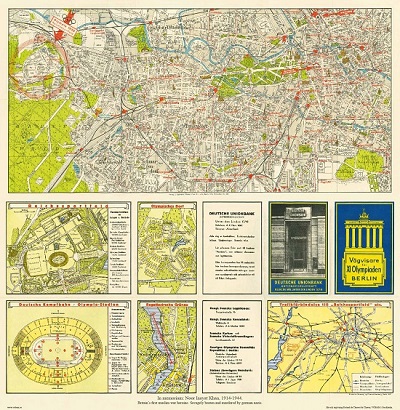
Vägvisare för XI Olympiaden i Berlin - 1936
Sachsen. - Blaeu 1643/44.
Olaus Magnus text till den berömda kartan "Carta Marina".
Texten finns även på katalanska, spanska och engelska.
Bureus karta över norden
Kartor och atlaser
Bilder och planschverk
Teckenförklaringar

Porträtt på Gerard Mercator och Jodocus Hondius.
"Striking image showing Mercator and Hondius in their idealized workshop.
This famous portrait of two of the most important mapmakers during the Golden Age of Dutch cartography was engraved by Coletta Hondius, as a tribute to her late husband, shortly after his death. Gerard Mercator is shown with his successor, Jodocus Hondius, seated at a table surrounded by the implements of their trade. The fine portrait is set within an elaborate strapwork framework that includes a wall map of Europe.
Gerard Mercator is renowned as the cartographer who created a world map representing new projections of sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation which, to this day, enhances the simplicity and safety of navigation. In his own day, Mercator was the world's most famous geographer. He created a number of wall maps early in his career, as well as one of the earliest modern world Atlases in 1595. Although this was the first appearance of the word Atlas in a geographical context, Mercator used it as a neologism for a treatise on the creation, history and description of the universe, not simply a collection of maps. He chose the word as a commemoration of King Atlas of Mauretania, whom he considered to be the first great geographer.
Jodocus Hondius was a Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe and for continuing publication of Gerard Mercator's World Atlas. He also helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century. In England, Hondius publicized the work of Francis Drake, who had made a circumnavigation of the world in the late 1570s. In 1604, he purchased the plates of Gerard Mercator's Atlas from Mercator's grandson and continued publication of the Atlas, adding his own maps over the next several decades. Hondius later published a pocket version Atlas Minor."