Kartograf. Gav ut en atlas i Portugal 1559
(RdeT.
1688-1766. Född och död i Paris.
Fransk geograf. Släkt med familjen Sanson. Blev tidigt inblandad i familjens kartografiska verksamhet och övertog företaget efter sin farbror Pierre Moulard Sanson. 1748 gav han ut en 'Petit Atlas' i två band (203 kartor) och 1757 'Atlas Universel' med 108 kartor. Ritningen av kartorna överläts åt duktiga konstnärer som även utsmyckade dem med kartuscher. Hovet, med Madame Pompadour i spetsen, gav sitt stöd till detta. 1762 utom 'Atlas portatif' innehållande 52 kartor. - Förutom atlaser gav han även ut andra geografiska verk, som 'Géographie sacrée et historique de l'Ancien et du Nouveau Testament' i tre band (1742) och 'Usage des globes celeste et terrestre' (1752). Robert de Vaugondy hade titeln som 'Géographe ordinaire du Roi' och var medlem av 'l'Académie Rle des Sciences et Belle-Lettres' i Nancy. Hans verk övertogs av sonen Didier Robert de Vaugondy (se denne).
Bland arbeten.
Petit Atlas.
Atlas Universel.
Atlas portatif.
Géographie sacrée et historique de l'Ancien et du Nouveau Testament.
Usage des globes celeste et terrestre.
Nouv. biogr. gen.
Se BLAEU, W. J.
Tooley.
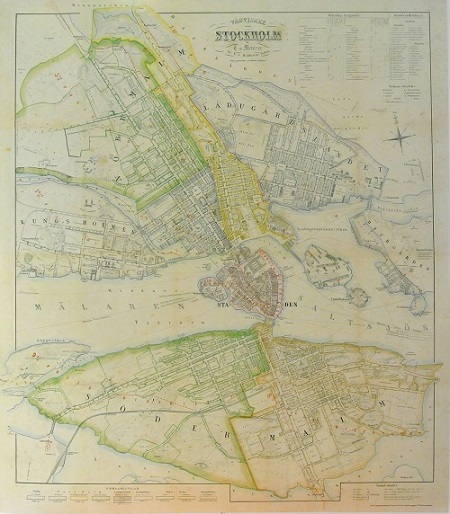
Stockholm - Mentzer ca 1860.
'Vue de l´Eglise St. Catharine a Stockholm' - 1700-tal.
Olaus Magnus text till den berömda kartan "Carta Marina".
Texten finns även på katalanska, spanska och engelska.
Bureus karta över norden
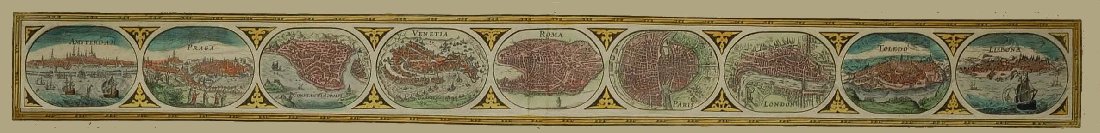
Kartor och atlaser
Bilder och planschverk
Teckenförklaringar

Porträtt på Gerard Mercator och Jodocus Hondius.
"Striking image showing Mercator and Hondius in their idealized workshop.
This famous portrait of two of the most important mapmakers during the Golden Age of Dutch cartography was engraved by Coletta Hondius, as a tribute to her late husband, shortly after his death. Gerard Mercator is shown with his successor, Jodocus Hondius, seated at a table surrounded by the implements of their trade. The fine portrait is set within an elaborate strapwork framework that includes a wall map of Europe.
Gerard Mercator is renowned as the cartographer who created a world map representing new projections of sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation which, to this day, enhances the simplicity and safety of navigation. In his own day, Mercator was the world's most famous geographer. He created a number of wall maps early in his career, as well as one of the earliest modern world Atlases in 1595. Although this was the first appearance of the word Atlas in a geographical context, Mercator used it as a neologism for a treatise on the creation, history and description of the universe, not simply a collection of maps. He chose the word as a commemoration of King Atlas of Mauretania, whom he considered to be the first great geographer.
Jodocus Hondius was a Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe and for continuing publication of Gerard Mercator's World Atlas. He also helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century. In England, Hondius publicized the work of Francis Drake, who had made a circumnavigation of the world in the late 1570s. In 1604, he purchased the plates of Gerard Mercator's Atlas from Mercator's grandson and continued publication of the Atlas, adding his own maps over the next several decades. Hondius later published a pocket version Atlas Minor."